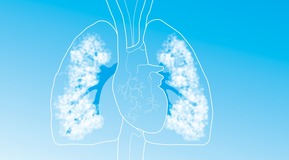

Many infants with hypoxic respiratory failure have a sporadic lung disease which means that the air flow (and therefore oxygenation) is good in some areas of the lungs and less good or non-existent in other areas.
When nitric oxide is inhaled, the constricted blood vessels in the lungs relax, so that the blood flow from the heart to the lungs increases, and the quantity of blood that goes outside the lungs decreases. The blood flow increases in those areas of the lungs where the air flow is greatest and where the best gas exchange can take place.
The pharmaceutical development of inhaled nitric oxide started in the 1980s by three researchers - Robert F. Furchgott, Louis Ignarro and Ferid Murad. They were awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine 1998.